Russian Bolonka Puppies Early Neurological Stimulation
Benefits of Early Neurological Stimulation for Russian Bolonka Puppies
About The Author:
Carmen L Battaglia holds a Ph.D. and Masters Degree from Florida State University. As an AKC judge, researcher and writer, he has been a leader in promotion of breeding better dogs and has written many articles and several books. Dr. Battaglia is also a popular TV and radio talk show speaker. His seminars on breeding dogs, selecting sires and choosing puppies have been well received by the breed clubs all over the country.
Carmen L Battaglia holds a Ph.D. and Masters Degree from Florida State University. As an AKC judge, researcher and writer, he has been a leader in promotion of breeding better dogs and has written many articles and several books. Dr. Battaglia is also a popular TV and radio talk show speaker. His seminars on breeding dogs, selecting sires and choosing puppies have been well received by the breed clubs all over the country.
The U.S. Military in their canine program developed a method that still serves as a guide to what works. In an effort to improve the performance of dogs used for military purposes, a program called "Bio Sensor" was developed. Later, it became known to the public as the "Super Dog" Program. Based on years of research, the military learned that early neurological stimulation exercises could have important and lasting effects. Their studies confirmed that there are specific time periods early in life when neurological stimulation has optimum results. The first period involves a window of time that begins at the third day of life and lasts until the sixteenth day. It is believed that because this interval of time is a period of rapid neurological growth and development, and therefore is of great importance to the individual.
The "Bio Sensor" program was also concerned with early neurological stimulation in order to give the dog a superior advantage. Its development utilized six exercises which were designed to stimulate the neurological system. Each workout involved handling puppies once each day. The workouts required handling them one at a time while performing a series of five exercises. Listed in order of preference, the handler starts with one pup and stimulates it using each of the five exercises. The handler completes the series from beginning to end before starting with the next pup. The handling of each pup once per day involves the following exercises:
The "Bio Sensor" program was also concerned with early neurological stimulation in order to give the dog a superior advantage. Its development utilized six exercises which were designed to stimulate the neurological system. Each workout involved handling puppies once each day. The workouts required handling them one at a time while performing a series of five exercises. Listed in order of preference, the handler starts with one pup and stimulates it using each of the five exercises. The handler completes the series from beginning to end before starting with the next pup. The handling of each pup once per day involves the following exercises:
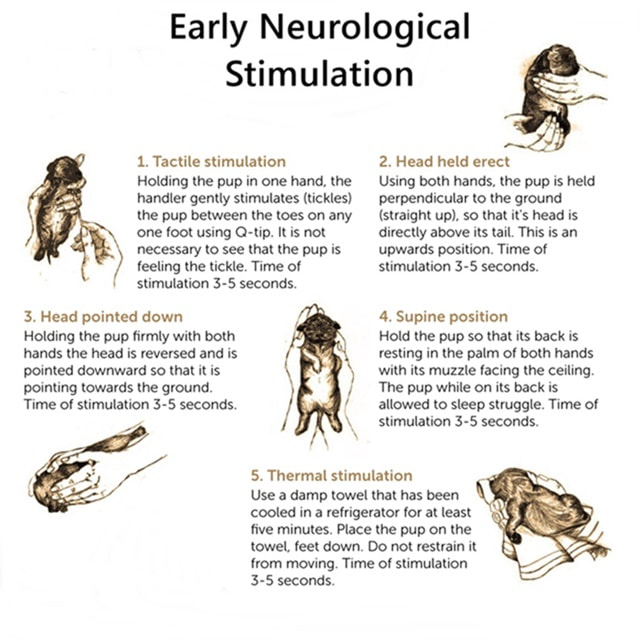
- Tactical stimulation (between toes)
- Head held erect
- Head pointed down
- Supine position
- Thermal stimulation
ENS Stimulation
- Tactile stimulation - holding the pup in one hand, the handler gently stimulates (tickles) the pup between the toes on any one foot using a Q-tip. It is not necessary to see that the pup is feeling the tickle. Time of stimulation 3 - 5 seconds.
- Head held erect - using both hands, the pup is held perpendicular to the ground, (straight up), so that its head is directly above its tail. This is an upwards position. Time of stimulation 3 - 5 seconds.
- Head pointed down - holding the pup firmly with both hands the head is reversed and is pointed downward so that it is pointing towards the ground. Time of stimulation 3 - 5 seconds.
- Supine position - hold the pup so that its back is resting in the palm of both hands with its muzzle facing the ceiling. The pup while on its back is allowed to sleep. Time of stimulation 3-5 seconds.
- Thermal stimulation—use a damp towel that has been cooled in a refrigerator for at least five minutes. Place the pup on the towel, feet down. Do not restrain it from moving. Time of stimulation 3-5 seconds.
These five exercises will produce neurological stimulations, none of which naturally occur during this early period of life. Experience shows that sometimes pups will resist these exercises, others will appear unconcerned. In either case a caution is offered to those who plan to use them. Do not repeat them more than once per day and do not extend the time beyond that recommended for each exercise.
Over stimulation of the neurological system can have adverse and detrimental results. These exercises impact the neurological system by kicking it into action earlier than would be normally expected, the result being an increased capacity that later will help to make the difference in its performance. Those who play with their pups and routinely handle them should continue to do so because the neurological exercises are not substitutions for routine handling, play socialization or bonding.
Benefits Of Stimulation
Five benefits have been observed in canines that were exposed to the Bio Sensor stimulation exercises. The benefits noted were:
Secondary effects were also noted regarding test performance. In simple problem solving tests using detours in a maze, the non-stimulated pups became extremely aroused, whined a great deal, and made many errors. Their stimulated littermates were less disturbed or upset by test conditions and when comparisons were made, the stimulated littermates were more calm in the test environment, made fewer errors and gave only an occasional distress sound when stressed.
A study found that while puppies are growing they are learning because their nervous systems are developing and storing information that may be of inestimable use at a later date. Studies by Scott and Fuller confirm that non-enriched pups, when given free choice, preferred to stay in their kennels. Other litter mates who were given only small amounts of outside stimulation between five and eight weeks of age were found to be very inquisitive and very active. When kennel doors were left open, the enriched pups would come bounding out while littermates who were not exposed to enrichment would remain behind. The non-stimulated pups would typically be fearful of unfamiliar objects and generally preferred to withdraw rather than investigate. Even well-bred pups of superior pedigrees would not explore or leave their kennels, and many were found difficult to train as adults. These pups, in many respects, were similar to deprived children. They acted as if they had become institutionalized, preferring the routine and safe environment of their kennel to the stimulating world outside their immediate place of residence.
- Improved cardio vascular performance (heart rate)
- Stronger heart beats
- Stronger adrenal glands
- More tolerance to stress
- Greater resistance to disease
Secondary effects were also noted regarding test performance. In simple problem solving tests using detours in a maze, the non-stimulated pups became extremely aroused, whined a great deal, and made many errors. Their stimulated littermates were less disturbed or upset by test conditions and when comparisons were made, the stimulated littermates were more calm in the test environment, made fewer errors and gave only an occasional distress sound when stressed.
A study found that while puppies are growing they are learning because their nervous systems are developing and storing information that may be of inestimable use at a later date. Studies by Scott and Fuller confirm that non-enriched pups, when given free choice, preferred to stay in their kennels. Other litter mates who were given only small amounts of outside stimulation between five and eight weeks of age were found to be very inquisitive and very active. When kennel doors were left open, the enriched pups would come bounding out while littermates who were not exposed to enrichment would remain behind. The non-stimulated pups would typically be fearful of unfamiliar objects and generally preferred to withdraw rather than investigate. Even well-bred pups of superior pedigrees would not explore or leave their kennels, and many were found difficult to train as adults. These pups, in many respects, were similar to deprived children. They acted as if they had become institutionalized, preferring the routine and safe environment of their kennel to the stimulating world outside their immediate place of residence.
To read this article in it's entirety please follow this link: breedingbetterdogs.com